
Cómo montar un servidor torrent para ver películas y series gratis (en español)
Lo pillo quieres desplegar un servidor torrent para ver series y películas pirata sin la molestia de leer toneladas de documentación. Bueno, esta es una guía directa para desplegar todo en sólo cinco minutos. Pongámonos manos a la obra. (Estoy asumiendo que sabes lo más básico de cómo manejar Linux, Docker y una terminal).
Paso #1: Instalar Docker y Docker-Compose.
[MANUAL] Primero, instala docker y docker-compose:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal stable"
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo usermod -aG docker <username>
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.26.0/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose[AUTOMÁTICO] O ejecuta este comando:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | sh
El contenido del script bash ejecutado, a fecha de 10/02/2023, es el siguiente:
#!/bin/sh
set -e
# Docker CE for Linux installation script
#
# See https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ for the installation steps.
#
# This script is meant for quick & easy install via:
# $ curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
# $ sh get-docker.sh
#
# For test builds (ie. release candidates):
# $ curl -fsSL https://test.docker.com -o test-docker.sh
# $ sh test-docker.sh
#
# NOTE: Make sure to verify the contents of the script
# you downloaded matches the contents of install.sh
# located at https://github.com/docker/docker-install
# before executing.
#
# Git commit from https://github.com/docker/docker-install when
# the script was uploaded (Should only be modified by upload job):
SCRIPT_COMMIT_SHA="66474034547a96caa0a25be56051ff8b726a1b28"
# strip "v" prefix if present
VERSION="${VERSION#v}"
# The channel to install from:
# * nightly
# * test
# * stable
# * edge (deprecated)
DEFAULT_CHANNEL_VALUE="stable"
if [ -z "$CHANNEL" ]; then
CHANNEL=$DEFAULT_CHANNEL_VALUE
fi
DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_URL="https://download.docker.com"
if [ -z "$DOWNLOAD_URL" ]; then
DOWNLOAD_URL=$DEFAULT_DOWNLOAD_URL
fi
DEFAULT_REPO_FILE="docker-ce.repo"
if [ -z "$REPO_FILE" ]; then
REPO_FILE="$DEFAULT_REPO_FILE"
fi
mirror=''
DRY_RUN=${DRY_RUN:-}
while [ $# -gt 0 ]; do
case "$1" in
--mirror)
mirror="$2"
shift
;;
--dry-run)
DRY_RUN=1
;;
--*)
echo "Illegal option $1"
;;
esac
shift $(( $# > 0 ? 1 : 0 ))
done
case "$mirror" in
Aliyun)
DOWNLOAD_URL="https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce"
;;
AzureChinaCloud)
DOWNLOAD_URL="https://mirror.azure.cn/docker-ce"
;;
esac
command_exists() {
command -v "$@" > /dev/null 2>&1
}
# version_gte checks if the version specified in $VERSION is at least
# the given CalVer (YY.MM) version. returns 0 (success) if $VERSION is either
# unset (=latest) or newer or equal than the specified version. Returns 1 (fail)
# otherwise.
#
# examples:
#
# VERSION=20.10
# version_gte 20.10 // 0 (success)
# version_gte 19.03 // 0 (success)
# version_gte 21.10 // 1 (fail)
version_gte() {
if [ -z "$VERSION" ]; then
return 0
fi
eval calver_compare "$VERSION" "$1"
}
# calver_compare compares two CalVer (YY.MM) version strings. returns 0 (success)
# if version A is newer or equal than version B, or 1 (fail) otherwise. Patch
# releases and pre-release (-alpha/-beta) are not taken into account
#
# examples:
#
# calver_compare 20.10 19.03 // 0 (success)
# calver_compare 20.10 20.10 // 0 (success)
# calver_compare 19.03 20.10 // 1 (fail)
calver_compare() (
set +x
yy_a="$(echo "$1" | cut -d'.' -f1)"
yy_b="$(echo "$2" | cut -d'.' -f1)"
if [ "$yy_a" -lt "$yy_b" ]; then
return 1
fi
if [ "$yy_a" -gt "$yy_b" ]; then
return 0
fi
mm_a="$(echo "$1" | cut -d'.' -f2)"
mm_b="$(echo "$2" | cut -d'.' -f2)"
if [ "${mm_a#0}" -lt "${mm_b#0}" ]; then
return 1
fi
return 0
)
is_dry_run() {
if [ -z "$DRY_RUN" ]; then
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
is_wsl() {
case "$(uname -r)" in
*microsoft* ) true ;; # WSL 2
*Microsoft* ) true ;; # WSL 1
* ) false;;
esac
}
is_darwin() {
case "$(uname -s)" in
*darwin* ) true ;;
*Darwin* ) true ;;
* ) false;;
esac
}
deprecation_notice() {
distro=$1
distro_version=$2
echo
printf "\033[91;1mDEPRECATION WARNING\033[0m\n"
printf " This Linux distribution (\033[1m%s %s\033[0m) reached end-of-life and is no longer supported by this script.\n" "$distro" "$distro_version"
echo " No updates or security fixes will be released for this distribution, and users are recommended"
echo " to upgrade to a currently maintained version of $distro."
echo
printf "Press \033[1mCtrl+C\033[0m now to abort this script, or wait for the installation to continue."
echo
sleep 10
}
get_distribution() {
lsb_dist=""
# Every system that we officially support has /etc/os-release
if [ -r /etc/os-release ]; then
lsb_dist="$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$ID")"
fi
# Returning an empty string here should be alright since the
# case statements don't act unless you provide an actual value
echo "$lsb_dist"
}
echo_docker_as_nonroot() {
if is_dry_run; then
return
fi
if command_exists docker && [ -e /var/run/docker.sock ]; then
(
set -x
$sh_c 'docker version'
) || true
fi
# intentionally mixed spaces and tabs here -- tabs are stripped by "<<-EOF", spaces are kept in the output
echo
echo "================================================================================"
echo
if version_gte "20.10"; then
echo "To run Docker as a non-privileged user, consider setting up the"
echo "Docker daemon in rootless mode for your user:"
echo
echo " dockerd-rootless-setuptool.sh install"
echo
echo "Visit https://docs.docker.com/go/rootless/ to learn about rootless mode."
echo
fi
echo
echo "To run the Docker daemon as a fully privileged service, but granting non-root"
echo "users access, refer to https://docs.docker.com/go/daemon-access/"
echo
echo "WARNING: Access to the remote API on a privileged Docker daemon is equivalent"
echo " to root access on the host. Refer to the 'Docker daemon attack surface'"
echo " documentation for details: https://docs.docker.com/go/attack-surface/"
echo
echo "================================================================================"
echo
}
# Check if this is a forked Linux distro
check_forked() {
# Check for lsb_release command existence, it usually exists in forked distros
if command_exists lsb_release; then
# Check if the `-u` option is supported
set +e
lsb_release -a -u > /dev/null 2>&1
lsb_release_exit_code=$?
set -e
# Check if the command has exited successfully, it means we're in a forked distro
if [ "$lsb_release_exit_code" = "0" ]; then
# Print info about current distro
cat <<-EOF
You're using '$lsb_dist' version '$dist_version'.
EOF
# Get the upstream release info
lsb_dist=$(lsb_release -a -u 2>&1 | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' | grep -E 'id' | cut -d ':' -f 2 | tr -d '[:space:]')
dist_version=$(lsb_release -a -u 2>&1 | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' | grep -E 'codename' | cut -d ':' -f 2 | tr -d '[:space:]')
# Print info about upstream distro
cat <<-EOF
Upstream release is '$lsb_dist' version '$dist_version'.
EOF
else
if [ -r /etc/debian_version ] && [ "$lsb_dist" != "ubuntu" ] && [ "$lsb_dist" != "raspbian" ]; then
if [ "$lsb_dist" = "osmc" ]; then
# OSMC runs Raspbian
lsb_dist=raspbian
else
# We're Debian and don't even know it!
lsb_dist=debian
fi
dist_version="$(sed 's/\/.*//' /etc/debian_version | sed 's/\..*//')"
case "$dist_version" in
11)
dist_version="bullseye"
;;
10)
dist_version="buster"
;;
9)
dist_version="stretch"
;;
8)
dist_version="jessie"
;;
esac
fi
fi
fi
}
do_install() {
echo "# Executing docker install script, commit: $SCRIPT_COMMIT_SHA"
if command_exists docker; then
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
Warning: the "docker" command appears to already exist on this system.
If you already have Docker installed, this script can cause trouble, which is
why we're displaying this warning and provide the opportunity to cancel the
installation.
If you installed the current Docker package using this script and are using it
again to update Docker, you can safely ignore this message.
You may press Ctrl+C now to abort this script.
EOF
( set -x; sleep 20 )
fi
user="$(id -un 2>/dev/null || true)"
sh_c='sh -c'
if [ "$user" != 'root' ]; then
if command_exists sudo; then
sh_c='sudo -E sh -c'
elif command_exists su; then
sh_c='su -c'
else
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
Error: this installer needs the ability to run commands as root.
We are unable to find either "sudo" or "su" available to make this happen.
EOF
exit 1
fi
fi
if is_dry_run; then
sh_c="echo"
fi
# perform some very rudimentary platform detection
lsb_dist=$( get_distribution )
lsb_dist="$(echo "$lsb_dist" | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')"
if is_wsl; then
echo
echo "WSL DETECTED: We recommend using Docker Desktop for Windows."
echo "Please get Docker Desktop from https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop"
echo
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
You may press Ctrl+C now to abort this script.
EOF
( set -x; sleep 20 )
fi
case "$lsb_dist" in
ubuntu)
if command_exists lsb_release; then
dist_version="$(lsb_release --codename | cut -f2)"
fi
if [ -z "$dist_version" ] && [ -r /etc/lsb-release ]; then
dist_version="$(. /etc/lsb-release && echo "$DISTRIB_CODENAME")"
fi
;;
debian|raspbian)
dist_version="$(sed 's/\/.*//' /etc/debian_version | sed 's/\..*//')"
case "$dist_version" in
11)
dist_version="bullseye"
;;
10)
dist_version="buster"
;;
9)
dist_version="stretch"
;;
8)
dist_version="jessie"
;;
esac
;;
centos|rhel|sles)
if [ -z "$dist_version" ] && [ -r /etc/os-release ]; then
dist_version="$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_ID")"
fi
;;
*)
if command_exists lsb_release; then
dist_version="$(lsb_release --release | cut -f2)"
fi
if [ -z "$dist_version" ] && [ -r /etc/os-release ]; then
dist_version="$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_ID")"
fi
;;
esac
# Check if this is a forked Linux distro
check_forked
# Print deprecation warnings for distro versions that recently reached EOL,
# but may still be commonly used (especially LTS versions).
case "$lsb_dist.$dist_version" in
debian.stretch|debian.jessie)
deprecation_notice "$lsb_dist" "$dist_version"
;;
raspbian.stretch|raspbian.jessie)
deprecation_notice "$lsb_dist" "$dist_version"
;;
ubuntu.xenial|ubuntu.trusty)
deprecation_notice "$lsb_dist" "$dist_version"
;;
fedora.*)
if [ "$dist_version" -lt 33 ]; then
deprecation_notice "$lsb_dist" "$dist_version"
fi
;;
esac
# Run setup for each distro accordingly
case "$lsb_dist" in
ubuntu|debian|raspbian)
pre_reqs="apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl"
if ! command -v gpg > /dev/null; then
pre_reqs="$pre_reqs gnupg"
fi
apt_repo="deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] $DOWNLOAD_URL/linux/$lsb_dist $dist_version $CHANNEL"
(
if ! is_dry_run; then
set -x
fi
$sh_c 'apt-get update -qq >/dev/null'
$sh_c "DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y -qq $pre_reqs >/dev/null"
$sh_c 'mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings && chmod -R 0755 /etc/apt/keyrings'
$sh_c "curl -fsSL \"$DOWNLOAD_URL/linux/$lsb_dist/gpg\" | gpg --dearmor --yes -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg"
$sh_c "chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg"
$sh_c "echo \"$apt_repo\" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list"
$sh_c 'apt-get update -qq >/dev/null'
)
pkg_version=""
if [ -n "$VERSION" ]; then
if is_dry_run; then
echo "# WARNING: VERSION pinning is not supported in DRY_RUN"
else
# Will work for incomplete versions IE (17.12), but may not actually grab the "latest" if in the test channel
pkg_pattern="$(echo "$VERSION" | sed "s/-ce-/~ce~.*/g" | sed "s/-/.*/g")"
search_command="apt-cache madison 'docker-ce' | grep '$pkg_pattern' | head -1 | awk '{\$1=\$1};1' | cut -d' ' -f 3"
pkg_version="$($sh_c "$search_command")"
echo "INFO: Searching repository for VERSION '$VERSION'"
echo "INFO: $search_command"
if [ -z "$pkg_version" ]; then
echo
echo "ERROR: '$VERSION' not found amongst apt-cache madison results"
echo
exit 1
fi
if version_gte "18.09"; then
search_command="apt-cache madison 'docker-ce-cli' | grep '$pkg_pattern' | head -1 | awk '{\$1=\$1};1' | cut -d' ' -f 3"
echo "INFO: $search_command"
cli_pkg_version="=$($sh_c "$search_command")"
fi
pkg_version="=$pkg_version"
fi
fi
(
pkgs="docker-ce${pkg_version%=}"
if version_gte "18.09"; then
# older versions didn't ship the cli and containerd as separate packages
pkgs="$pkgs docker-ce-cli${cli_pkg_version%=} containerd.io"
fi
if version_gte "20.10" && [ "$(uname -m)" = "x86_64" ]; then
# also install the latest version of the "docker scan" cli-plugin (only supported on x86 currently)
pkgs="$pkgs docker-scan-plugin"
fi
if version_gte "20.10"; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras$pkg_version"
fi
if version_gte "23.0"; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-buildx-plugin"
fi
if ! is_dry_run; then
set -x
fi
$sh_c "DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y -qq $pkgs >/dev/null"
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
centos|fedora|rhel)
if [ "$(uname -m)" != "s390x" ] && [ "$lsb_dist" = "rhel" ]; then
echo "Packages for RHEL are currently only available for s390x."
exit 1
fi
if [ "$lsb_dist" = "fedora" ]; then
pkg_manager="dnf"
config_manager="dnf config-manager"
enable_channel_flag="--set-enabled"
disable_channel_flag="--set-disabled"
pre_reqs="dnf-plugins-core"
pkg_suffix="fc$dist_version"
else
pkg_manager="yum"
config_manager="yum-config-manager"
enable_channel_flag="--enable"
disable_channel_flag="--disable"
pre_reqs="yum-utils"
pkg_suffix="el"
fi
repo_file_url="$DOWNLOAD_URL/linux/$lsb_dist/$REPO_FILE"
(
if ! is_dry_run; then
set -x
fi
$sh_c "$pkg_manager install -y -q $pre_reqs"
$sh_c "$config_manager --add-repo $repo_file_url"
if [ "$CHANNEL" != "stable" ]; then
$sh_c "$config_manager $disable_channel_flag docker-ce-*"
$sh_c "$config_manager $enable_channel_flag docker-ce-$CHANNEL"
fi
$sh_c "$pkg_manager makecache"
)
pkg_version=""
if [ -n "$VERSION" ]; then
if is_dry_run; then
echo "# WARNING: VERSION pinning is not supported in DRY_RUN"
else
pkg_pattern="$(echo "$VERSION" | sed "s/-ce-/\\\\.ce.*/g" | sed "s/-/.*/g").*$pkg_suffix"
search_command="$pkg_manager list --showduplicates 'docker-ce' | grep '$pkg_pattern' | tail -1 | awk '{print \$2}'"
pkg_version="$($sh_c "$search_command")"
echo "INFO: Searching repository for VERSION '$VERSION'"
echo "INFO: $search_command"
if [ -z "$pkg_version" ]; then
echo
echo "ERROR: '$VERSION' not found amongst $pkg_manager list results"
echo
exit 1
fi
if version_gte "18.09"; then
# older versions don't support a cli package
search_command="$pkg_manager list --showduplicates 'docker-ce-cli' | grep '$pkg_pattern' | tail -1 | awk '{print \$2}'"
cli_pkg_version="$($sh_c "$search_command" | cut -d':' -f 2)"
fi
# Cut out the epoch and prefix with a '-'
pkg_version="-$(echo "$pkg_version" | cut -d':' -f 2)"
fi
fi
(
pkgs="docker-ce$pkg_version"
if version_gte "18.09"; then
# older versions didn't ship the cli and containerd as separate packages
if [ -n "$cli_pkg_version" ]; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-ce-cli-$cli_pkg_version containerd.io"
else
pkgs="$pkgs docker-ce-cli containerd.io"
fi
fi
if version_gte "20.10" && [ "$(uname -m)" = "x86_64" ]; then
# also install the latest version of the "docker scan" cli-plugin (only supported on x86 currently)
pkgs="$pkgs docker-scan-plugin"
fi
if version_gte "20.10"; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras$pkg_version"
fi
if version_gte "23.0"; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-buildx-plugin"
fi
if ! is_dry_run; then
set -x
fi
$sh_c "$pkg_manager install -y -q $pkgs"
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
sles)
if [ "$(uname -m)" != "s390x" ]; then
echo "Packages for SLES are currently only available for s390x"
exit 1
fi
if [ "$dist_version" = "15.3" ]; then
sles_version="SLE_15_SP3"
else
sles_minor_version="${dist_version##*.}"
sles_version="15.$sles_minor_version"
fi
opensuse_repo="https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/security:SELinux/$sles_version/security:SELinux.repo"
repo_file_url="$DOWNLOAD_URL/linux/$lsb_dist/$REPO_FILE"
pre_reqs="ca-certificates curl libseccomp2 awk"
(
if ! is_dry_run; then
set -x
fi
$sh_c "zypper install -y $pre_reqs"
$sh_c "zypper addrepo $repo_file_url"
if ! is_dry_run; then
cat >&2 <<-'EOF'
WARNING!!
openSUSE repository (https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/security:SELinux) will be enabled now.
Do you wish to continue?
You may press Ctrl+C now to abort this script.
EOF
( set -x; sleep 30 )
fi
$sh_c "zypper addrepo $opensuse_repo"
$sh_c "zypper --gpg-auto-import-keys refresh"
$sh_c "zypper lr -d"
)
pkg_version=""
if [ -n "$VERSION" ]; then
if is_dry_run; then
echo "# WARNING: VERSION pinning is not supported in DRY_RUN"
else
pkg_pattern="$(echo "$VERSION" | sed "s/-ce-/\\\\.ce.*/g" | sed "s/-/.*/g")"
search_command="zypper search -s --match-exact 'docker-ce' | grep '$pkg_pattern' | tail -1 | awk '{print \$6}'"
pkg_version="$($sh_c "$search_command")"
echo "INFO: Searching repository for VERSION '$VERSION'"
echo "INFO: $search_command"
if [ -z "$pkg_version" ]; then
echo
echo "ERROR: '$VERSION' not found amongst zypper list results"
echo
exit 1
fi
search_command="zypper search -s --match-exact 'docker-ce-cli' | grep '$pkg_pattern' | tail -1 | awk '{print \$6}'"
# It's okay for cli_pkg_version to be blank, since older versions don't support a cli package
cli_pkg_version="$($sh_c "$search_command")"
pkg_version="-$pkg_version"
fi
fi
(
pkgs="docker-ce$pkg_version"
if version_gte "18.09"; then
if [ -n "$cli_pkg_version" ]; then
# older versions didn't ship the cli and containerd as separate packages
pkgs="$pkgs docker-ce-cli-$cli_pkg_version containerd.io"
else
pkgs="$pkgs docker-ce-cli containerd.io"
fi
fi
if version_gte "20.10"; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras$pkg_version"
fi
if version_gte "23.0"; then
pkgs="$pkgs docker-buildx-plugin"
fi
if ! is_dry_run; then
set -x
fi
$sh_c "zypper -q install -y $pkgs"
)
echo_docker_as_nonroot
exit 0
;;
*)
if [ -z "$lsb_dist" ]; then
if is_darwin; then
echo
echo "ERROR: Unsupported operating system 'macOS'"
echo "Please get Docker Desktop from https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop"
echo
exit 1
fi
fi
echo
echo "ERROR: Unsupported distribution '$lsb_dist'"
echo
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 1
}
# wrapped up in a function so that we have some protection against only getting
# half the file during "curl | sh"
do_install
Paso #2: Descargar mi carpeta de configuración.
La forma más rápida de configurar esto es tomar prestada mi configuración, confía en mí. Descarga esta carpeta comprimida en tu servidor.
Paso #3: Crear el archivo Docker-Compose.
Bien, dentro de la carpeta de configuración (descomprímela), verás un archivo docker-compose.yml. Debe de tener este contenido:
version: "3.7"
services:
jellyfin:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/jellyfin:latest
container_name: jellyfin
environment: &env
- PUID=<Enter your USER_ID>
- PGID=<Enter your GROUP_ID>
- TZ=<Enter your time zone>
volumes:
- ./config/jellyfin:/config
- ./library/series:/data/series
- ./library/movies:/data/movies
ports:
- 8096:8096
- 8920:8920 #optional
- 7359:7359/udp #optional
- 1900:1900/udp #optional
restart: &restartpolicy unless-stopped
radarr:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/radarr:latest
container_name: radarr
environment: *env
volumes:
- ./config/arr/radarr/config:/config
- ./library/movies:/data/movies #optional
- ./downloads:/downloads #optional
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
ports:
- 7878:7878
restart: *restartpolicy
sonarr:
container_name: sonarr
image: cr.hotio.dev/hotio/sonarr:latest
restart: *restartpolicy
logging:
driver: json-file
network_mode: bridge
ports:
- 8989:8989
environment: *env
volumes:
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
- ./config/arr/sonarr/config:/config
- ./downloads:/downloads #optional
qbittorrent:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/qbittorrent:latest
container_name: qbittorrent
environment:
- PUID=<Enter your USER_ID>
- PGID=<Enter your GROUP_ID>
- TZ=<Enter your time zone>
- WEBUI_PORT=9095
volumes:
- ./torrent/qbittorrent/config:/config
- ./downloads:/downloads
ports:
- 9095:9095
- 6881:6881
- 6881:6881/udp
restart: *restartpolicy
prowlarr:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/prowlarr:develop
container_name: prowlarr
environment: *env
volumes:
- ./torrent/prowlarr/config:/config
ports:
- 9696:9696
restart: *restartpolicyPaso #4: Ejecuta tus contenedores!
sudo docker-compose up -dPaso #5: Vamos a configurar nuestros indexadores.
En primer lugar, quiero aclarar que no es necesario tener un nombre de dominio. Con saber la IP de tu servidor, y a qué puertos tienes que acceder para conectarte a las interfaces web, es más que suficiente.
Personalmente, uso ingressRoutes (usando traefik como Ingress Controller) para conectarme a estas interfaces web gracias a los subdominios. Pero dejo a vuestra elección cómo hacerlo, podéis usar Nginx reverse proxy, nginx manager, traefik reverse proxy en Docker....
Ok, primero tenemos que conectarnos a Prowlarr (usa http://<tuIP>
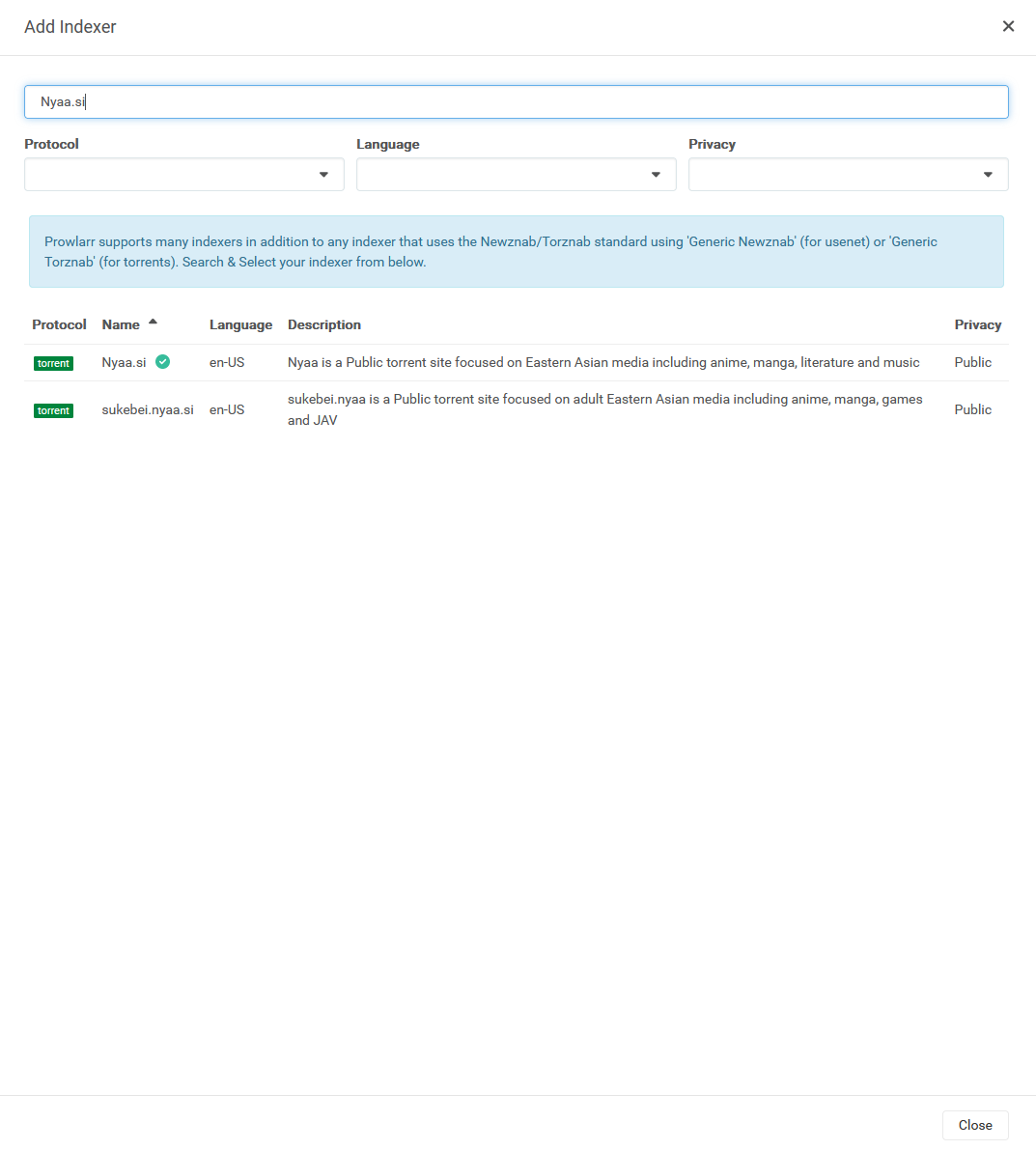
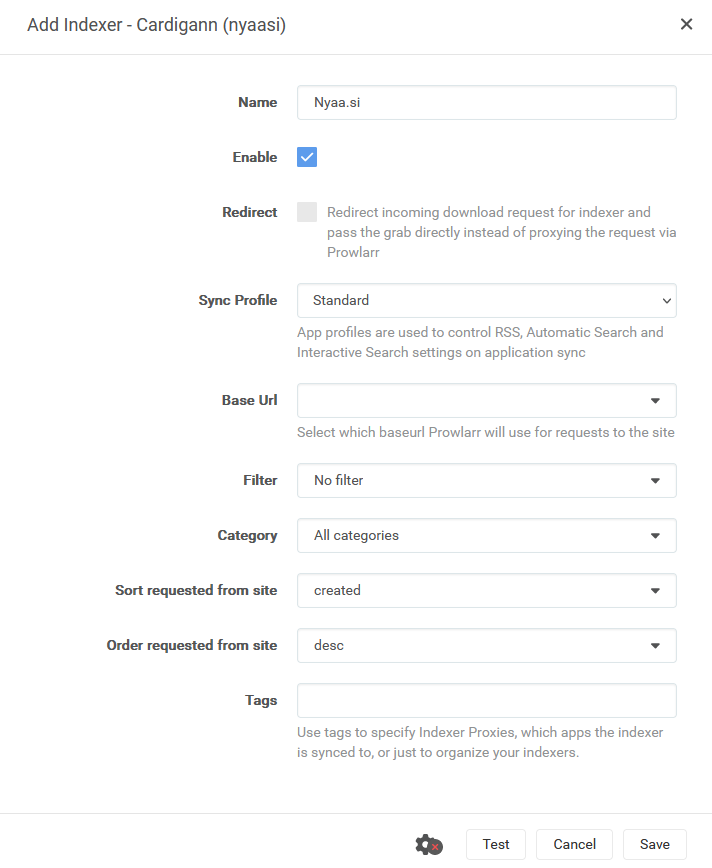
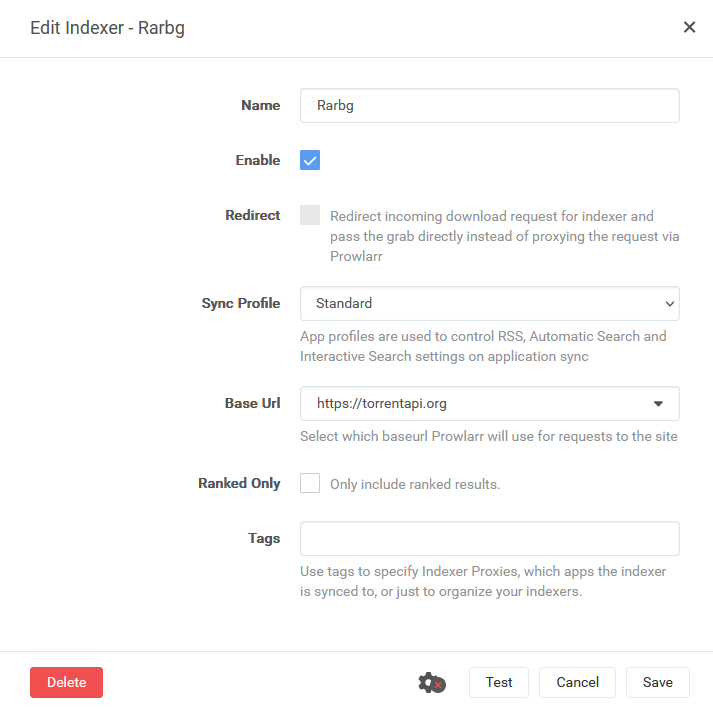
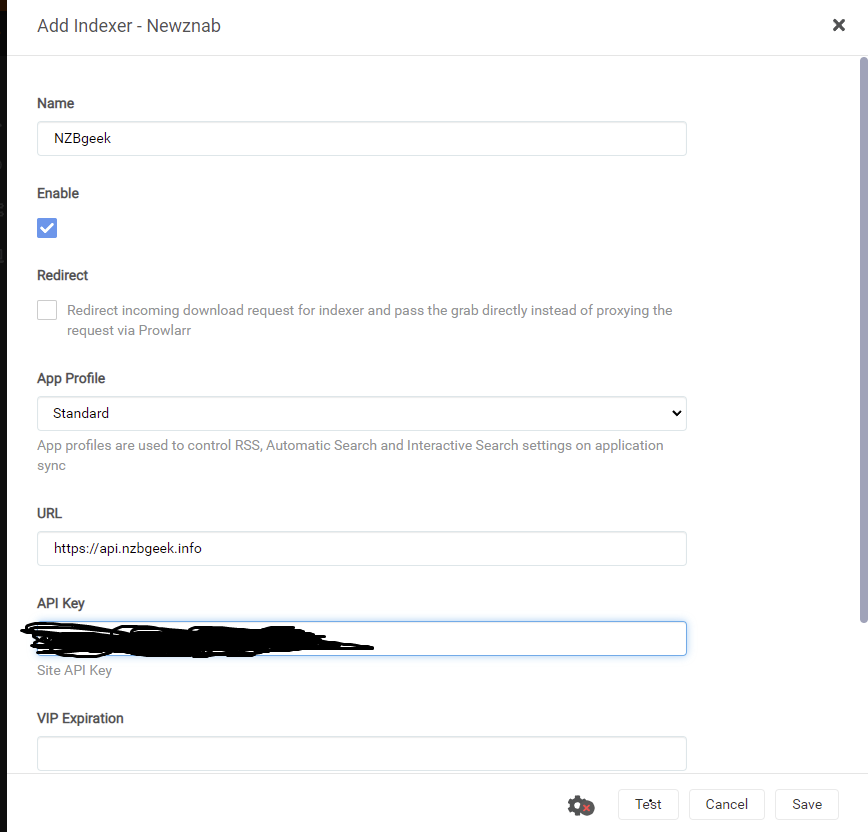
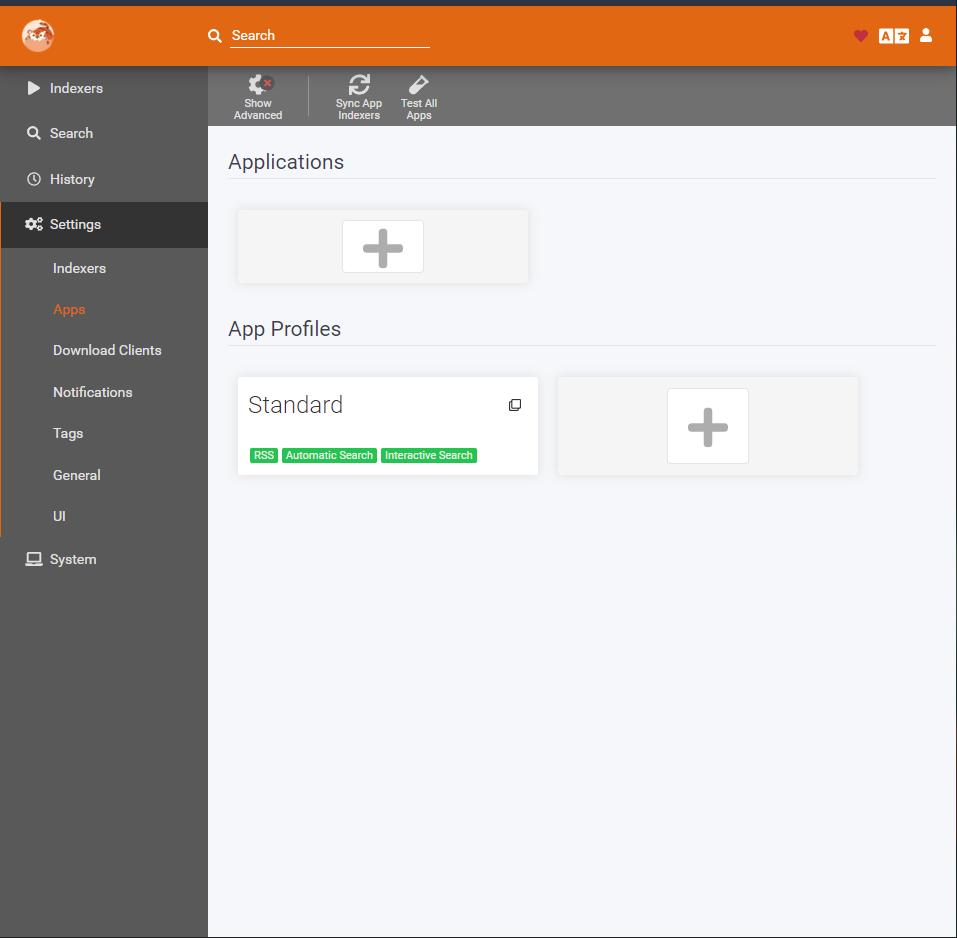
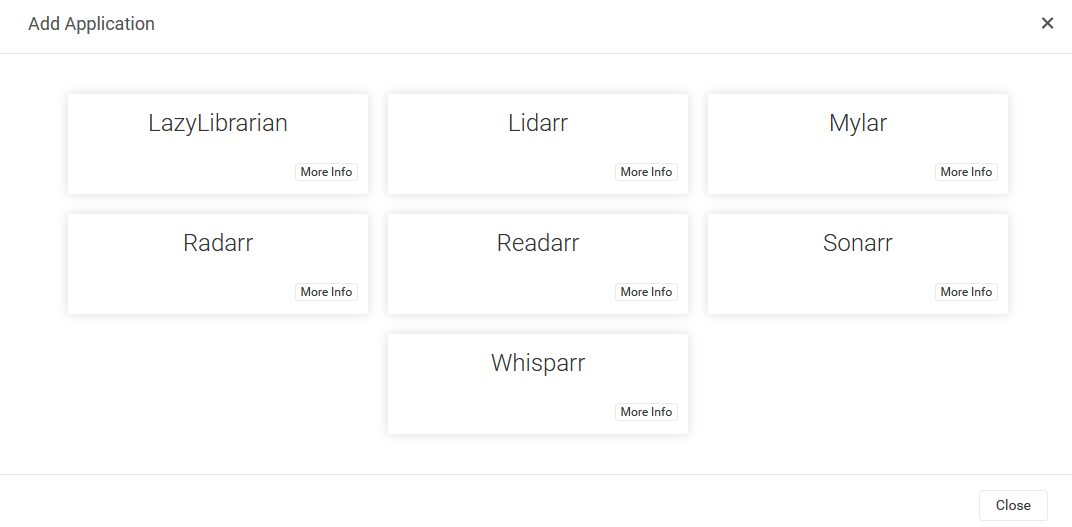
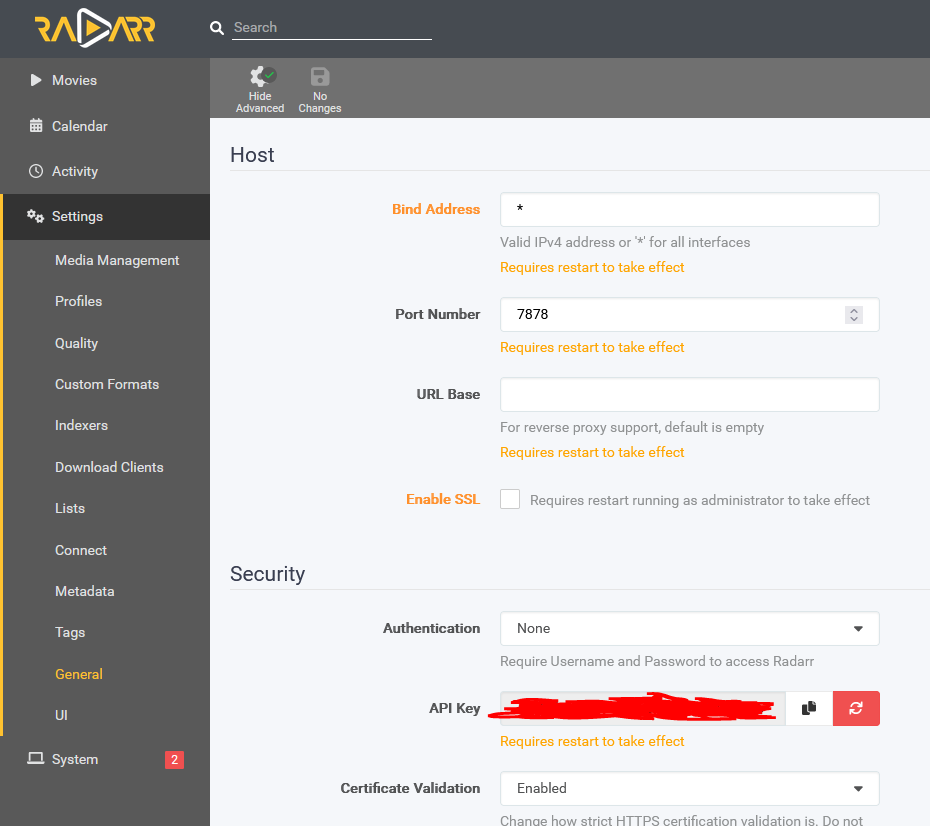
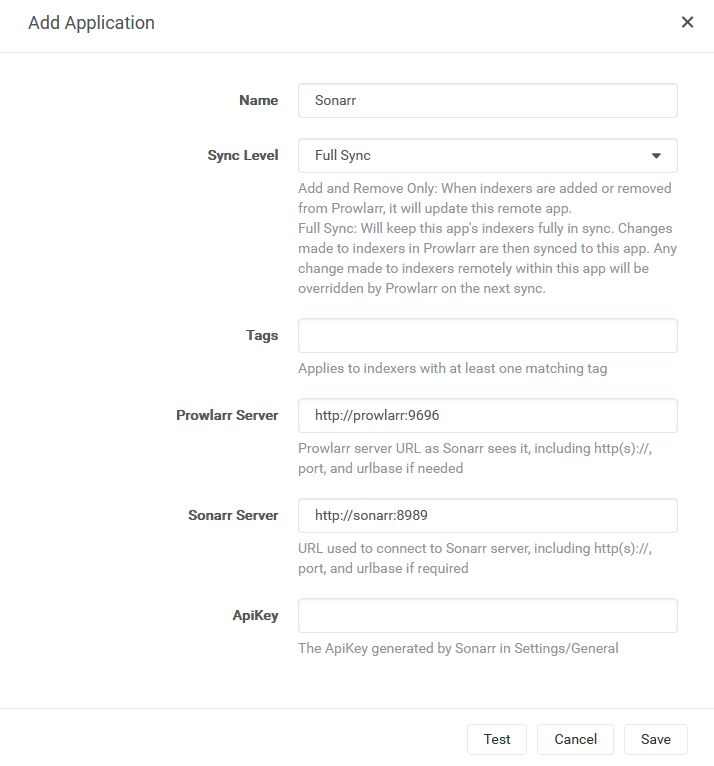
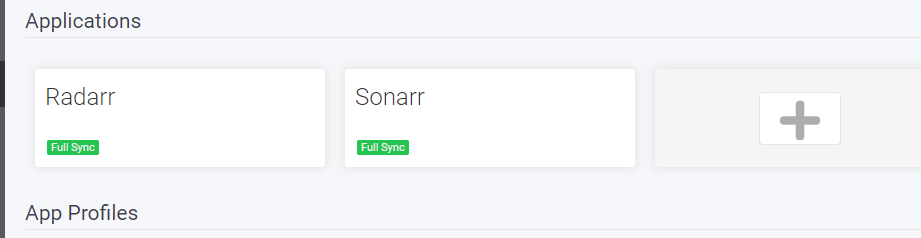
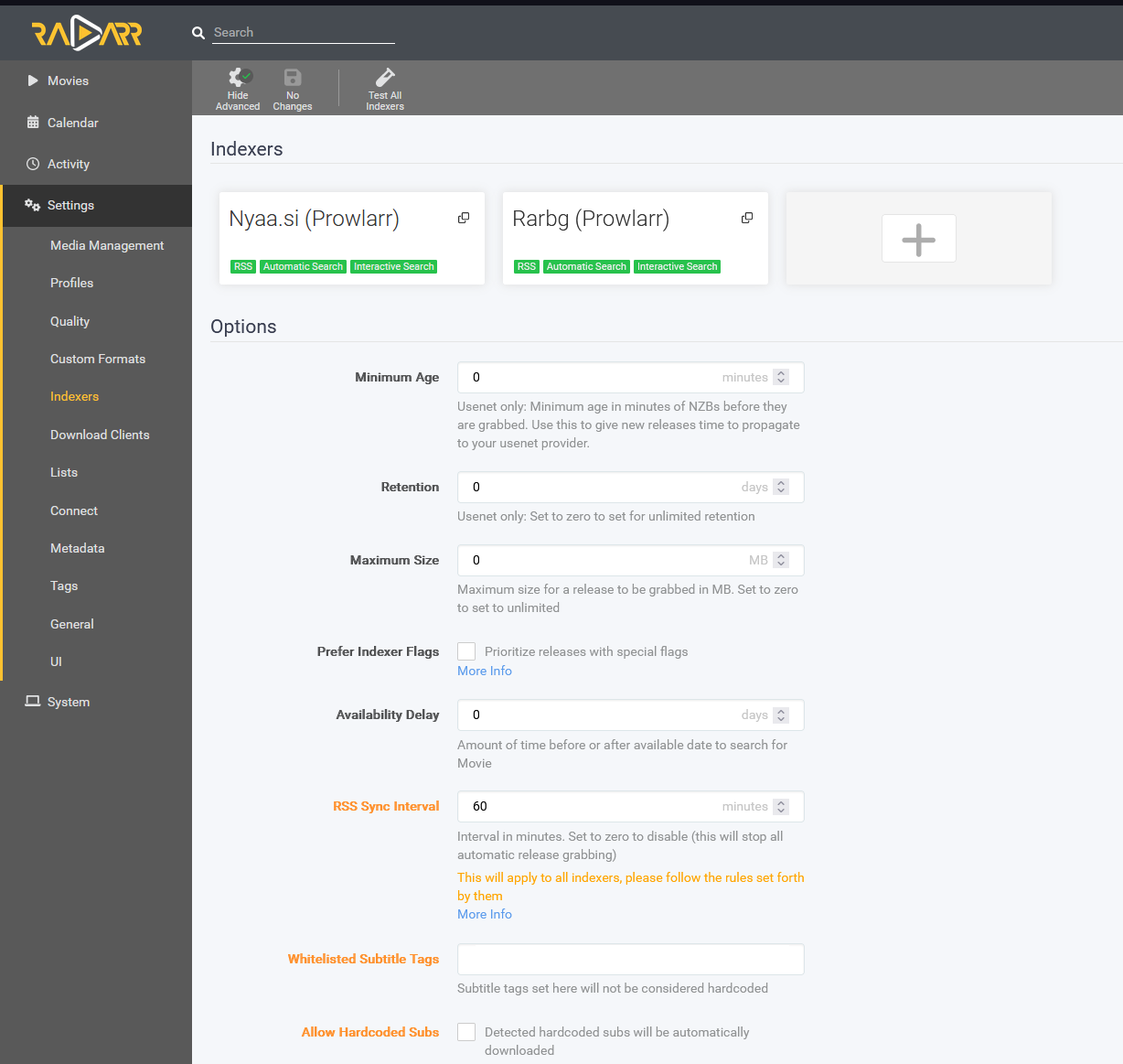
Paso #6: Configura tu cliente torrent.
"Pero quiero usar usenet en lugar de torrents". Vale, pues haré una guía más completa teniendo en cuenta usenet. Pero por ahora, sigamos con los torrents.
En cualquier caso, aquí tienes una lista de "Pros y contras".
Y aquí tienes algo de documentación adicional.
Bien, para conectarnos a la webUI de qbittorrent, tenemos que usar el puerto 9095 (puedes cambiarlo en el archivo docker-compose.yml).
Conéctate a http://<tuIP>
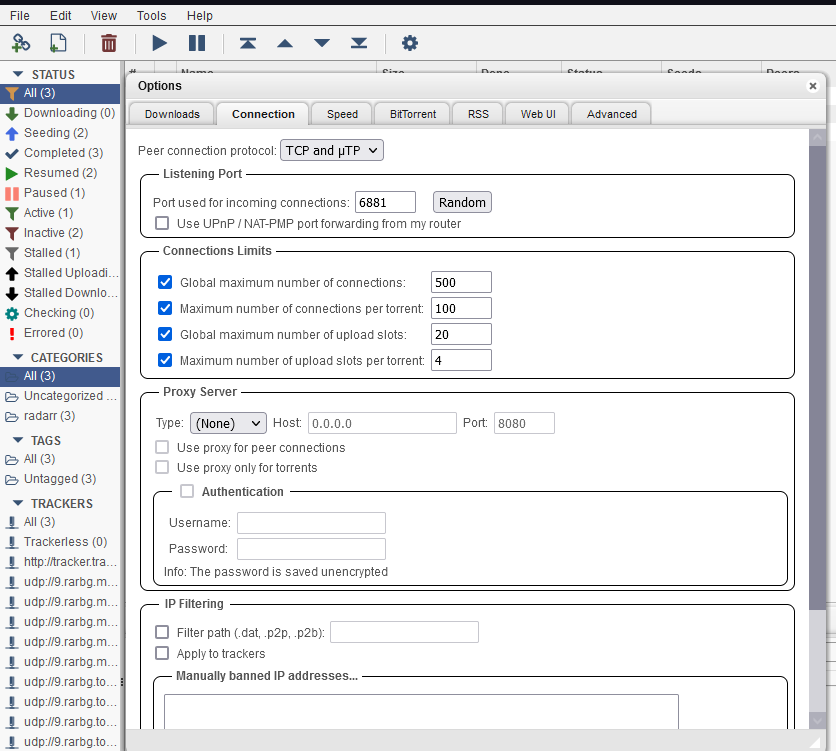
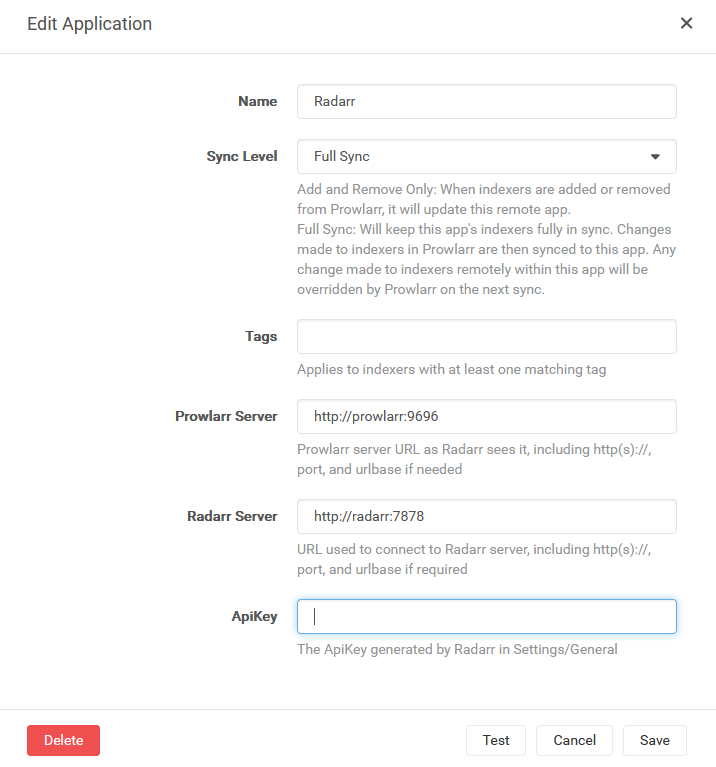
Paso #7: Configura Radarr y Sonarr
Radarr y Sonarr son muy similares. Así que la configuración que vamos a hacer es exactamente la misma para ambos. Vamos a usar Radarr como ejemplo pero la configuración es la misma para Sonarr también. Vamos a empezar.
Ve a http://<tuIP>
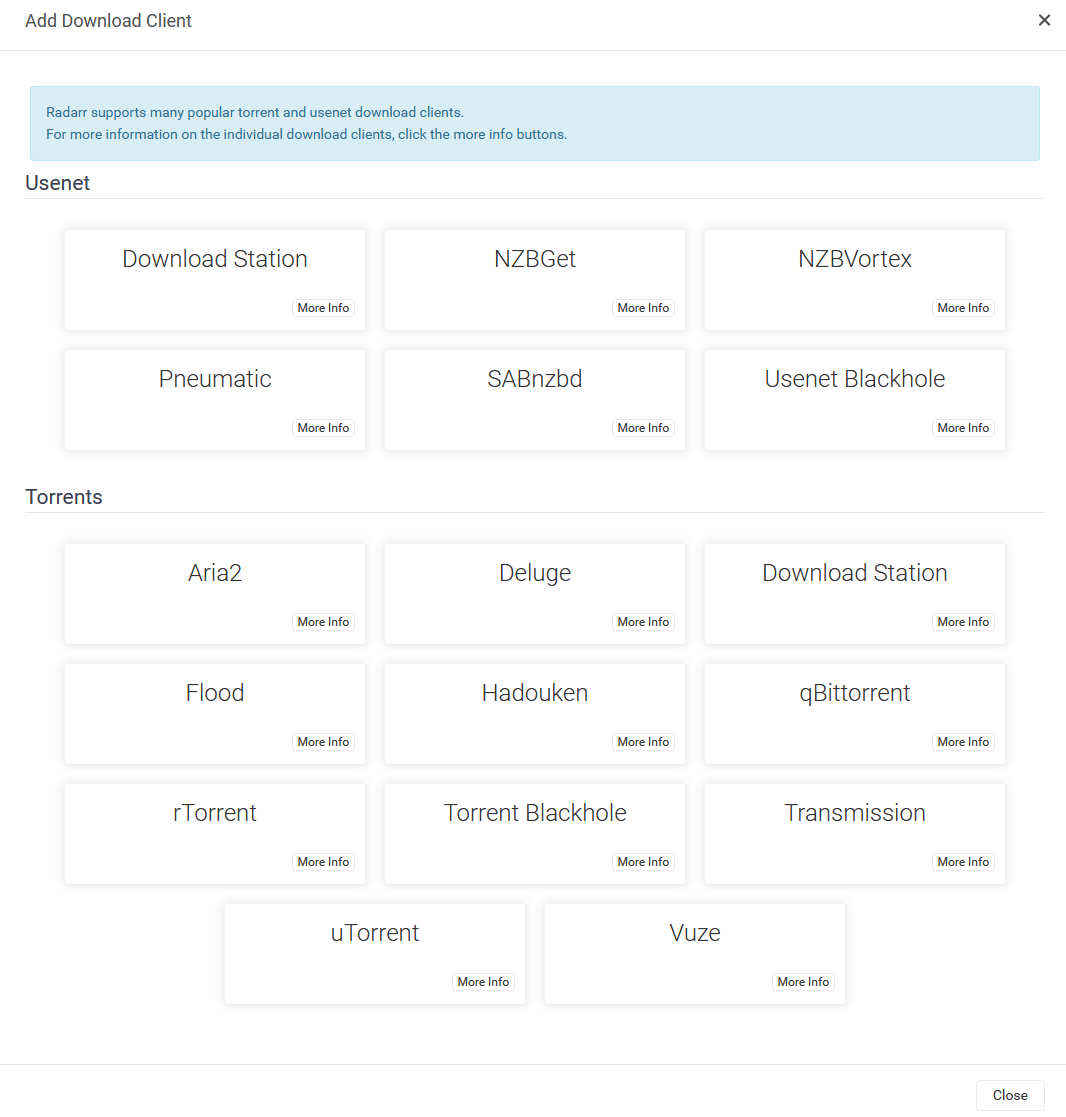
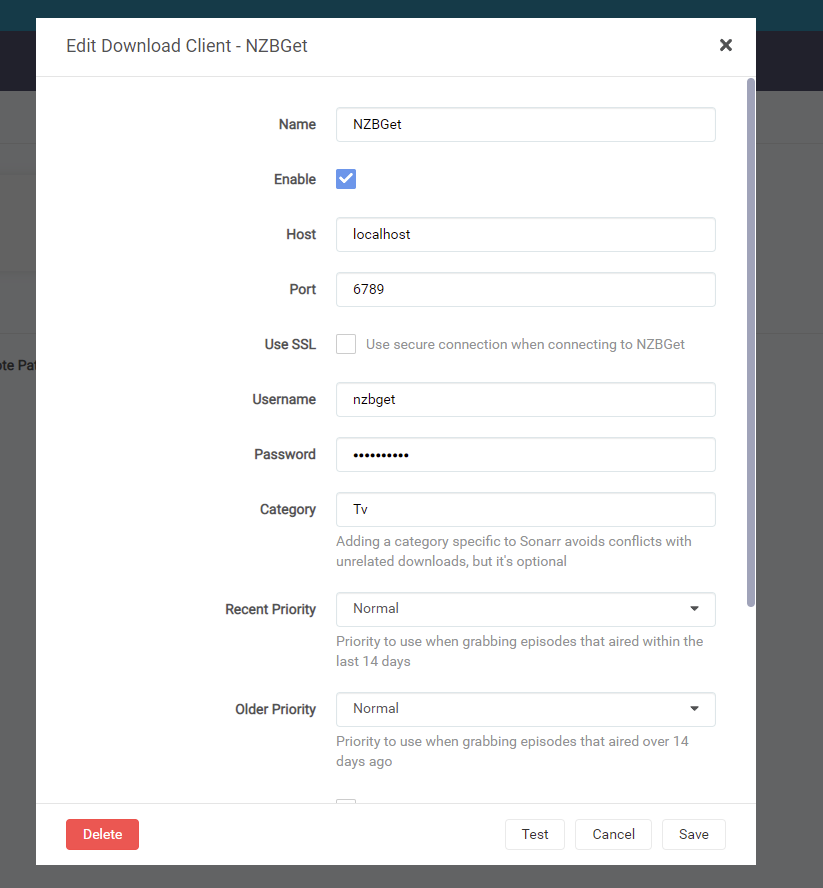
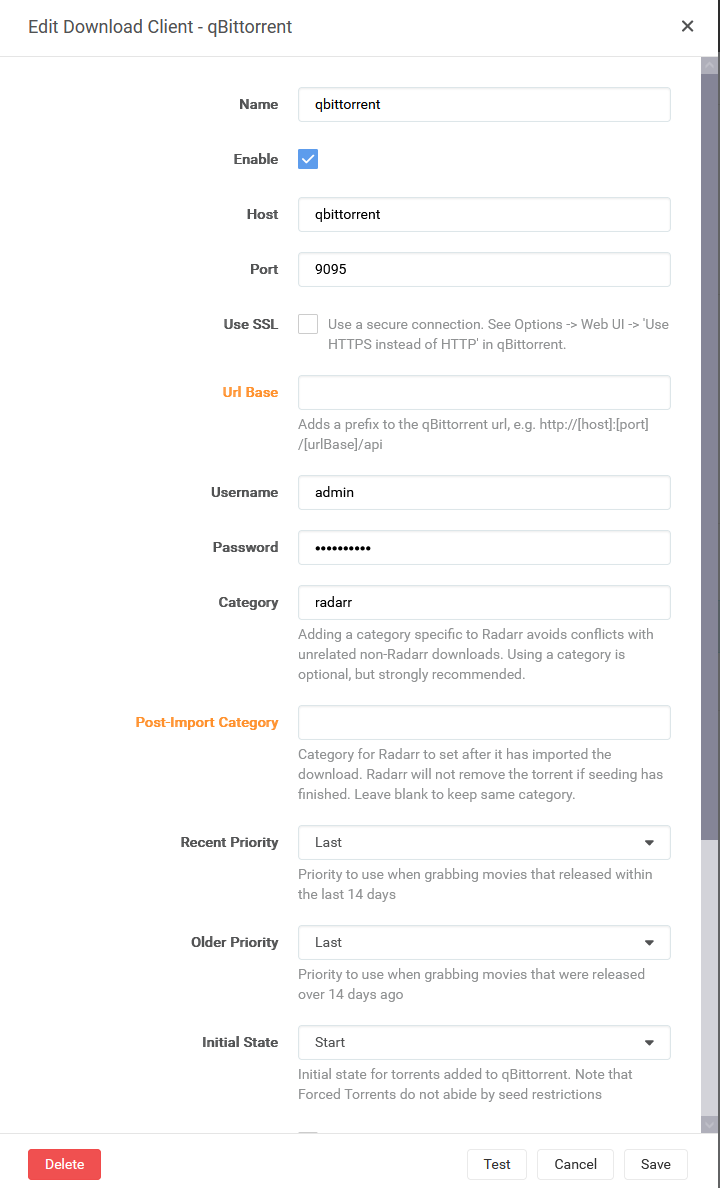
Repite este proceso para Sonarr.
Paso #8: Configura tus perfiles de calidad.
Este paso es importante, tanto es así que hay gente que ha creado herramientas para optimizar este paso, usando configuraciones especiales.
Dejo aquí algo de documentación.
Ve a la pestaña de Perfiles, tanto en Radarr como en Sonarr:
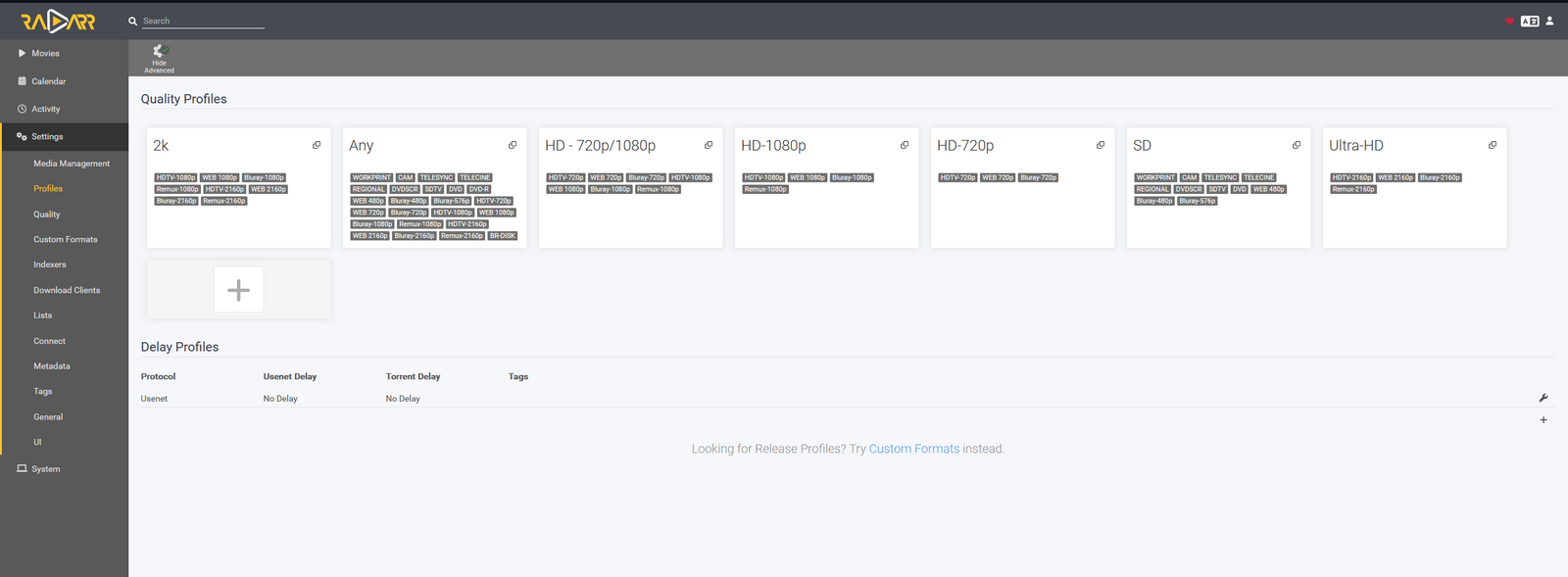
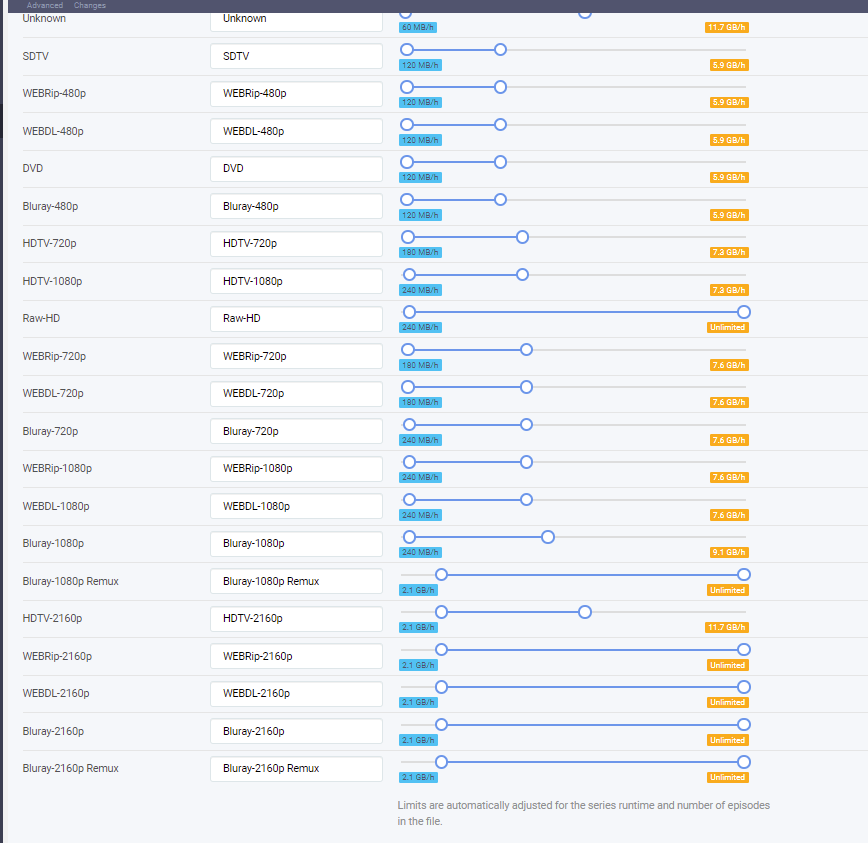
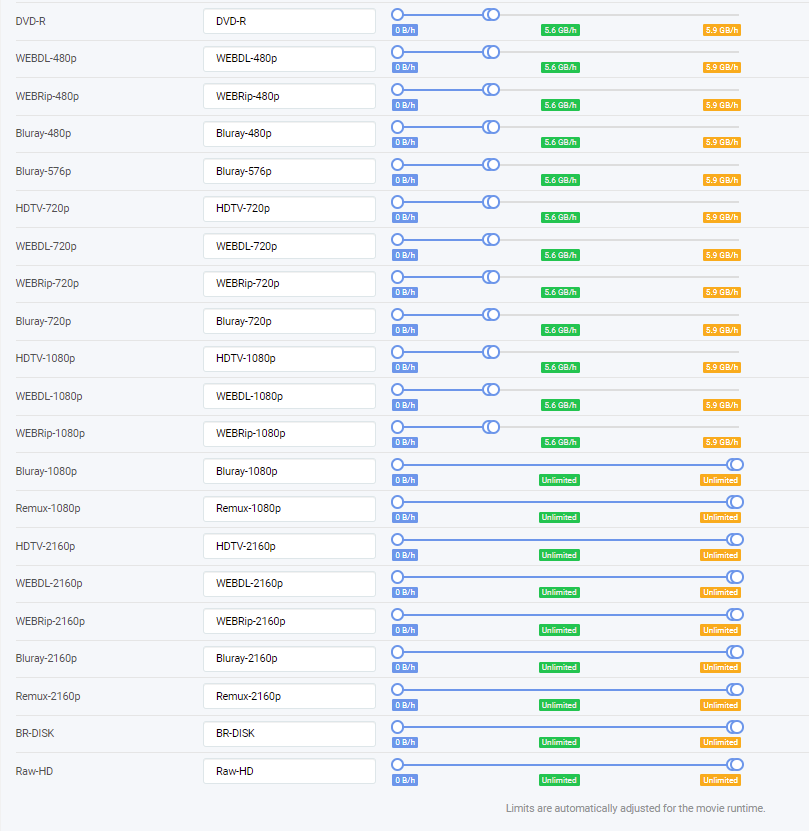
Dejo aquí mis perfiles "Any":
Ahora, vamos a buscar algunas series y películas. En Radarr o Sonarr, ve a la página de inicio, busca la película o la serie que quieres ver y selecciónala. Deberías ver una pantalla como ésta:
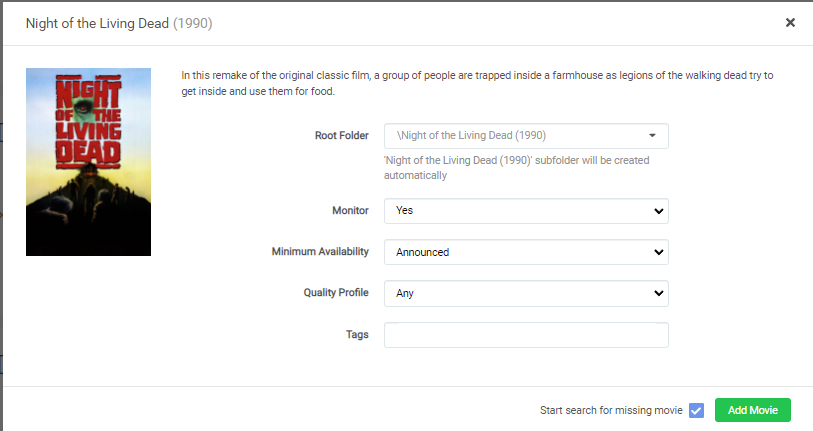
Y una vez hagas esto, haz click en el poster de la película:
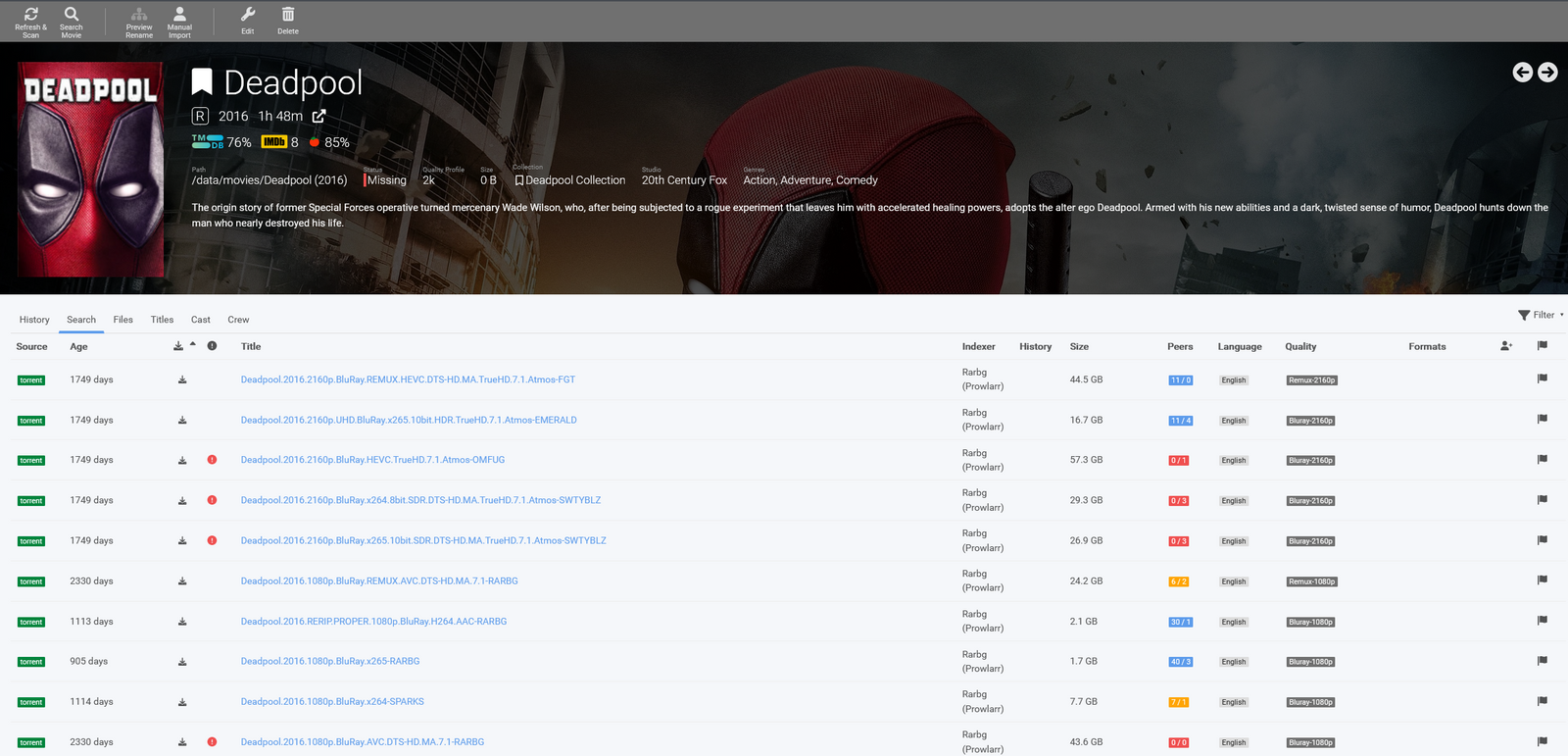
Paso #9: Configura tu Media Server favorito.
En esta guía usaré Jellyfin, pero siéntete libre de usar cualquier otro, como Plex, qflood... simplemente cambia el docker-compose.yml para desplegar tu aplicación seleccionada.
Para Jellyfin, ve a http://<tuIP>:8096.
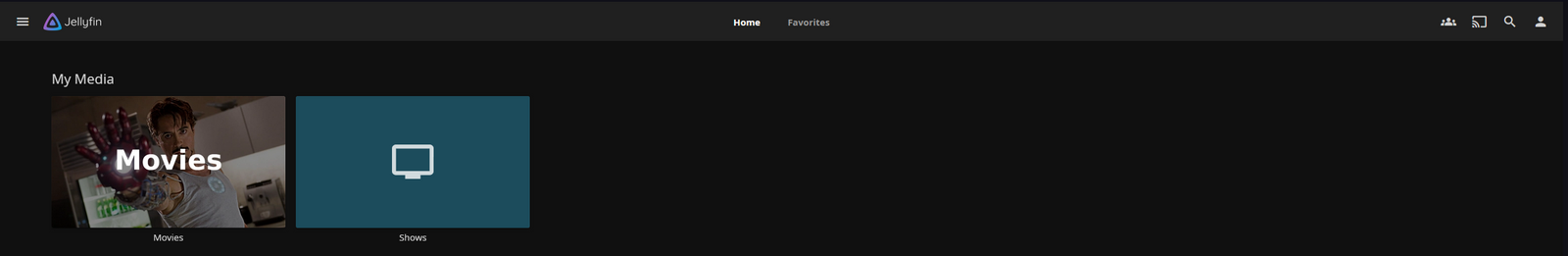
Ok, si haces click en "Movies", habrá una lista de películas descargadas.

¡Y eso es todo, amigos! Ya tienes un sitio de torrents funcionando en tu servidor sin ninguna molestia.
En cuanto sea posible subiré una configuración más compleja, con bazarr para los subtítulos, y ajustes de calidad tanto para sonarr como para radarr usando recyclarr, usando también jellyseer para gestionar las peticiones de los usuarios.
Disfruta de la piratería!
Recomendaciones
Configura un servicio de bazarr para obtener subtítulos. Haré una guía al respecto lo antes posible.
Establece un servicio para gestionar las solicitudes de los usuarios. Yo uso Jellyseer para este propósito. Haré una guía sobre esto también. Lo prometo.
No montes tu torrent server en un servidor que no es de su propiedad, como una instancia de AWS. Pueden bannearte por eso.
Si quieres retocar un poco Jellyfin, con temas y demás, mira este vídeo.
Extra Docker-Compose
Si prefieres usar traefik como proxy inverso y qflood como Media Server, puedes usar este archivo docker-compose.yml en lugar del ya escrito en la carpeta comprimida jellyfin.7z:
version: '3'
services:
qflood:
image: cr.hotio.dev/hotio/qflood:release-4.3.9--4.7.0
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=100
- UMASK=002
- TZ=Europe/Madrid
- FLOOD_AUTH=true
ports:
- "51413:51413"
volumes:
- '/your/pathstorage/data/qflood:/config'
- '/your/path:/data'
- '/storage/shared/bittorrent:/downloads'
labels:
- traefik.enable=true
- traefik.http.routers.flood.entryPoints=web-secure
- traefik.http.routers.flood.rule=Host(`yourdomain`)
- traefik.http.services.flood.loadbalancer.server.port=3000
- traefik.http.routers.flood.service=flood
- traefik.http.routers.qbittorrent.entryPoints=web-secure
- traefik.http.routers.qbittorrent.rule=Host(`yourdomain`)
- traefik.http.services.qbittorrent.loadbalancer.server.port=8080
- traefik.http.routers.qbittorrent.service=qbittorrent
networks:
- rflood
restart: unless-stopped
prowlarr:
image: cr.hotio.dev/hotio/prowlarr:nightly
ports:
- "9696:9696"
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- UMASK=002
- TZ=Europe/Madrid
volumes:
- /your/path:/config
labels:
- traefik.enable=true
- traefik.http.routers.prowlarr.entryPoints=web-secure
- traefik.http.routers.prowlarr.rule=Host(`yourdomain`)
- traefik.http.services.prowlarr.loadbalancer.server.port=9696
networks:
- rflood
restart: unless-stopped
sonarr:
image: cr.hotio.dev/hotio/sonarr
ports:
- "8989:8989"
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=100
- UMASK=002
- TZ=Europe/Madrid
volumes:
- './config/arr/sonarr/config:/config'
- '/storage/shared/bittorrent:/storage'
labels:
- traefik.enable=true
- traefik.http.routers.sonarr.entryPoints=web-secure
- traefik.http.routers.sonarr.rule=Host(`yourdomain`)
- traefik.http.services.sonarr.loadbalancer.server.port=8989
networks:
- rflood
restart: unless-stopped
radarr:
image: cr.hotio.dev/hotio/radarr
ports:
- "7878:7878"
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=100
- UMASK=002
- TZ=Europe/Madrid
volumes:
- './config/arr/radarr/config:/config'
- '/storage/shared/bittorrent:/storage'
labels:
- traefik.enable=true
- traefik.http.routers.radarr.entryPoints=web-secure
- traefik.http.routers.radarr.rule=Host(`yourdomain`)
- traefik.http.services.radarr.loadbalancer.server.port=7878
networks:
- rflood
restart: unless-stopped
bazarr:
image: hotio/bazarr
ports:
- "6767:6767"
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- UMASK=002
- TZ=Europe/Madrid
volumes:
- ./config/arr/bazarr/config:/config
- /storage/shared/bittorrent/media:/storage/media
labels:
- traefik.enable=true
- traefik.http.routers.bazarr.entryPoints=web-secure
- traefik.http.routers.bazarr.rule=Host(`yourdomain`)
- traefik.http.services.bazarr.loadbalancer.server.port=6767
networks:
- rflood
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
rflood:
driver: bridgeComo puedes ver, tienes total libertad para elegir dónde quieres almacenar tus datos y tu configuración. Establece una ruta donde diga "/tu/ruta". Además, se incluye el servicio bazarr (para los subtítulos).
Créditos
Gracias a mi amigo Edu, por descubrirme Servarr.
https://morrismotel.com/servarr-pt3b-prowlarr-sonarr-radarr/